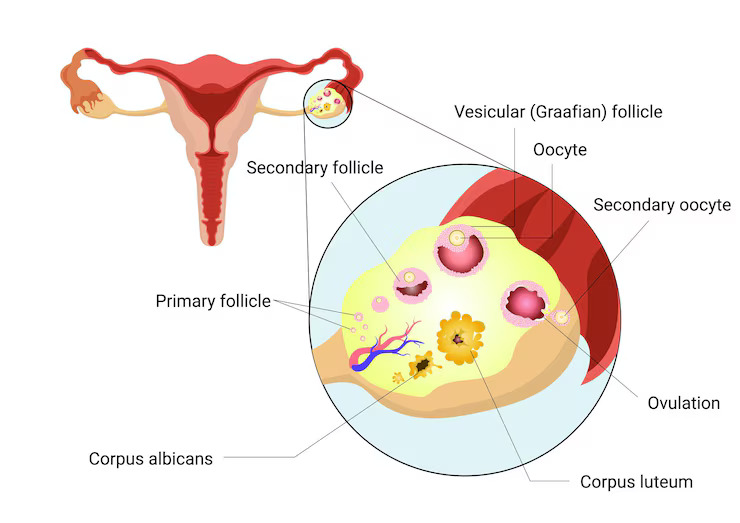
Ovaries are a vital part of the female reproductive system, and they house the eggs in ovarian follicles. The tiny, fluid-filled sacs are ovarian follicles where the eggs stay from the time of a female’s birth until the egg is mature enough to descend down the fallopian tube during the ovulation phase.
The tiny fluid sacs surround the immature eggs in the ovary while they are mature enough to go down the fallopian tube for fertilisation. The eggs start to mature once a woman reaches puberty and starts menstruating. The ovarian follicles are important as they influence the menstrual cycle of a woman. During every menstrual cycle, a single egg grows to maturity and travels down the follicle that ruptures during ovulation to release the mature egg. When a woman reaches puberty, 300,000 to 4,00,000 follicles are left. However, only an ultrasound of the pelvic region can determine how many follicles are left and a woman’s fertility levels.
4 Stages of Ovarian Follicle
Let’s take a look at the different stages of ovarian follicle development for a better understanding:
Primary Follicle: This is the first stage when the ovarian follicle starts to mature and is ready for release for ovulation. At this stage, the germinal cells start to surround the follicles to form layers that are called primary follicles.
Secondary Follicle: At this stage, the primary follicles start to mature further, and from the additional layers, granular cells are formed around the primary follicles. These granular cells are secondary follicles.
Tertiary Follicle: At the third stage, two more additional layers are formed around the secondary follicle. These additional layers are theca interna, and externa. It also has an antrum—a space that’s filled with fluid. This tertiary follicle is much larger.
Graafian Follicle: This is the last stage as the oocyte matures and gets ready for release. This is the ovulation stage, where the corpus luteum forms to support and promote embryo implantation once it’s fertilised by the sperm.
How Do Ovarian Follicles Affect Fertility?
Most women after the age of 35 face trouble conceiving, and that’s when doctors suggest a fertility test. The test measures her ovarian reserves by counting the number of follicles left. This is because throughout the lifecycle of a female, many follicles disintegrate and are reabsorbed by the body. As one ages, the rate of diminishment increases, which depletes the ovarian reserve of a woman. The number of ovarian follicles present in a woman’s body is related directly to her fertility.
Ovarian Follicles & It’s Importance
Ovarian follicles nurture, protect, and secrete hormones that help eggs mature and get released during ovulation. If ovarian follicles are not present, the eggs won’t mature and cannot be fertilised. In fact, fertility issues are related to follicles and can lead to conditions like PCOS and premature ovarian insufficiency. You can learn more about these from a healthcare professional at IRM.
The Usual Count of Antral Follicles
It’s a normal antral follicle count when each ovary has 5 to 10 antral follicles and is around 2 to 100 mm in diameter. However, the antral follicle is indirectly proportional to ageing. The higher the age of a female, the lower the antral follicle count.
The Dominant Follicle of The Ovary
Out of the numerous follicles, the one that matures is the dominant follicle. In the natural menstrual cycle, one or two dominant follicles are present, but with fertility treatment at IRM and certain medications given by our team of doctors, the mature egg count can increase, thereby increasing your chances of conceiving.
The Empty-Follicle Syndrome
The empty-follicle syndrome is also called EFS. Follicular aspiration helps stimulate the ovaries to retrieve more oocytes, and when this process fails, then it’s called EFS. That’s when medical intervention is necessary, as healthcare professionals administer HCG to increase the number of oocytes for retrieval. If HCG levels are optimised and there are no oocytes for retrieval, then it is a genuine EFS, and if there are no oocytes for low HCG, then it is a false EFS.
Takeaway
Ovarian follicles are vital to determining female fertility. If there is a lack of follicles in the ovary or any malfunctioning of the ovarian follicles, then it directly impacts a woman’s fertility. However, a healthcare professional can help you get the right treatment.